International Health Organization
global commitment to health and well-being
Health for all
International Health Organization
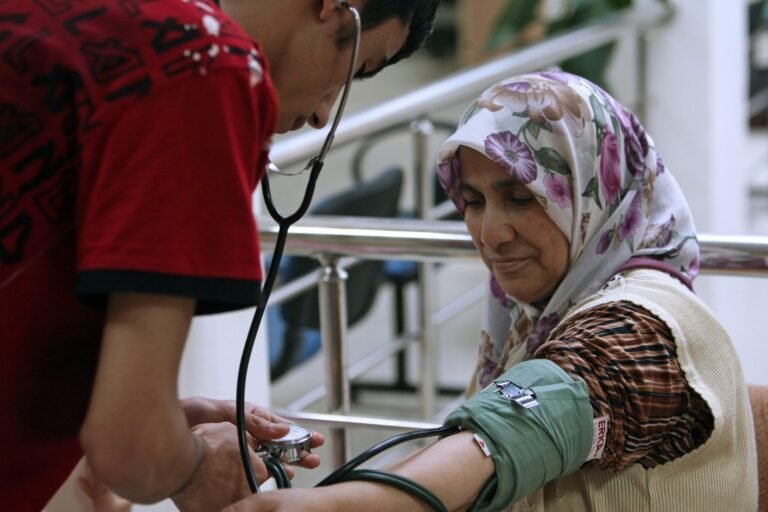
It is an independent non-profit organization that aims to promote public health at the global level by launching effective initiatives and innovative programs that promote the well-being of individuals and communities. The organization works to address contemporary health challenges such as chronic diseases, maternal and child health, awareness of the importance of prevention and primary health care, focusing on supporting the most vulnerable communities.
International health
Health Ethics from a global perspective
-
It focuses on achieving justice and equality in healthcare and promoting transparency in policies.
Overview -
It ensures the protection of participants and their rights by adhering to informed consent and distributing benefits fairly.
Health Research -
A balance between protecting public health and safeguarding the rights of individuals without discrimination.
Optimization
Health for all
Overview
Ethical issues in the field of Health and health care address multiple topics such as reproductive health, obligations of states in the provision of care and measures to combat infectious diseases. Historically, scientists have been discussing these issues since the beginning of Medicine, and international standards of Health Ethics appeared after the Nuremberg experiments of 1947. The Nuremberg Code contains important principles for health research involving human participants, and with increasing health challenges, the need for clear Ethics in health policies and practices to ensure justice and equality is emerging.

Health for all
Health Research Ethics
Research ethics governs the norms of behavior of scientific researchers, and adherence to ethical principles is vital for protecting the dignity, rights and well-being of participants. Human research is any activity in the fields of Social Sciences, biomedicine, behavior or epidemiology that involves the systematic collection or analysis of data with the aim of generating new knowledge. This includes any interaction with participants, whether through direct intervention or changing their environment, the possibility of identifying them through biological materials or medical records.
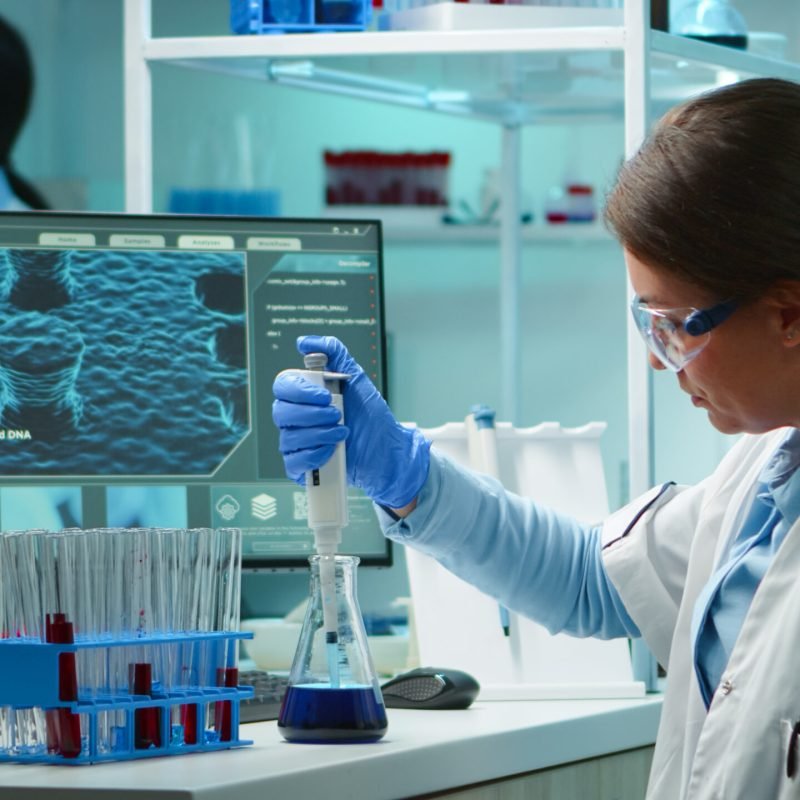

Health for all
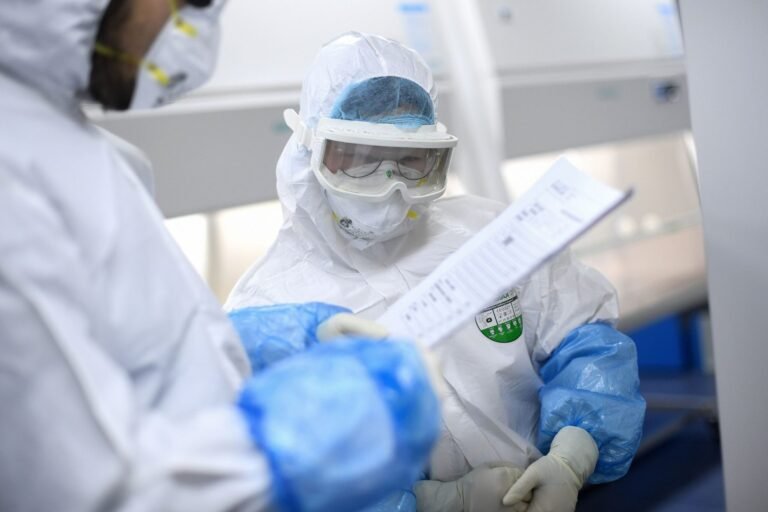
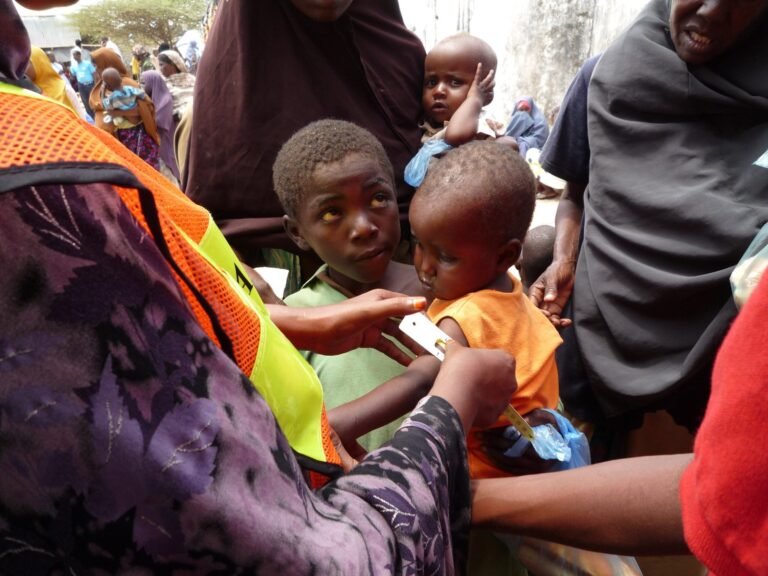
Ethical issues in the fight against infectious diseases
Many ethical issues pose complex challenges that require careful handling by researchers and stakeholders. These issues include questions related to fairness in the distribution of resources, the protection of vulnerable individuals, and respect for patients ' treatment-related decisions.
These challenges are particularly evident in the context of infectious diseases, where the importance of cooperation between communities and health authorities to respond to crises is highlighted. Responding to these challenges requires a deep understanding of the ethical dimensions associated with public health, reflecting the need to direct efforts towards ensuring the rights and well-being of individuals.
Donate now
Make a difference
Through your donation, you contribute to supporting key initiatives aimed at combating infectious diseases and improving health care. Discover inspiring success stories that show the positive impact of your contributions.
Major developments
Notable stops in the history of World Health
Founding of the World Health Organization
The organization was established with the aim of promoting global health and providing assistance to countries .
Founding of the World Health Organization
1948
Alta conference (Alma-Ata)
The conference was held, which declared primary health care as a basic human right, and emphasized the importance of providing health care for all.
Alta conference (Alma-Ata)
1978
Anti-AIDS program
The launch of the global program to combat HIV (HIV) and AIDS, which contributed to the provision of support and resources to the affected countries.
Anti-AIDS program
1988
Declaration of war on tuberculosis
Launched the Global Tuberculosis Control Program, which contributed to raising awareness about this disease and improving the response of global health systems to it.
Declaration of war on tuberculosis
2003
Health for all
Partners of success
We believe that true success does not come by individual effort, but by joint efforts and a unified vision.